The COVID-19 pandemic has stimulated digitalization to an unprecedented extent. From remote workforces to open banking or e-purchasing, virtually EVERYONE – from individuals to big corporations – is increasingly becoming dependent on technology, turning the need for secure digitalization into a pressing global issue. The latest cybercrime statistics and reports make it obvious that embracing hyper-connectivity is far from being risk-free. In an always-connected world that has urged cybercriminals to diversify and perfect their cyber-weapons and tactics, spam has turned not only into a daily annoyance but also into an insidious threat that preys upon human nature.
Spam – the hidden threats behind this deceptive practice
According to FinancesOnline, emails are – by far – the leading malware carriers, with laptops and desktops being the most vulnerable devices to cybercrimes.
Spam preys upon human weakness. According to The Hacker News, human error continues to be the main security threat. While it is true that human error encompasses a wide variety of potentially harmful actions (e.g. weak passwords usage, deficient password storage, accidental release/publication of sensitive data, sending confidential/sensitive information to the wrong recipient, etc.), falling victim to malicious spam (e.g. malware spam, phishing emails, smishing, etc.) can have disastrous consequences. For a better understanding, let’s take a look at the famous Crelan case. Back in 2016, Crelan – a Belgian bank – lost no less than €70 million to BEC (i.e. Business Email Compromise) scammers. How do these attacks work? By compromising the email account of the CEO or some other high-level manager, impersonating him/her, and ordering employees to make payments to an account owned by the scammers. Unfortunately, this is not the only notorious and costly case. Even Facebook and Google fell victims to phishing scams.
Advertising Vs. Scams
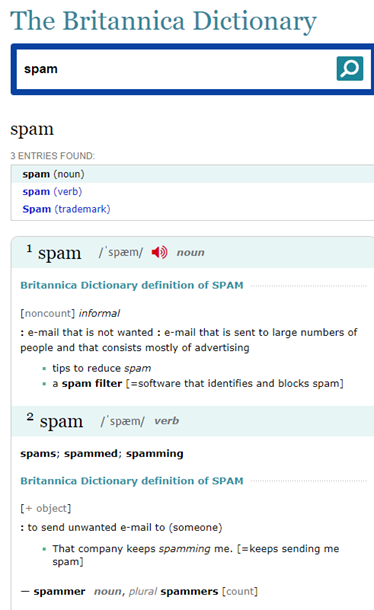
The Britannica Dictionary defines spam as follows:
Even though spam is often pure advertising covering a wide range of products and services (from adult content to personal finance or even anti-spam solutions), some other bulk mailings are nothing but outrageous fraud attempts.
Prominent types of malicious spam
Email phishing
This is one of the most common types of attacks. Scammers use impersonation to lure victims into downloading malicious content. The victims are redirected to malicious websites designed to steal credentials or make them install malicious code.
Spear phishing
The main difference between email phishing and spear phishing is that the latter targets specific victims within an organization. Cybercriminals use public sources (e.g. the company’s website) to gather information about a specific individual (i.e. real name, position inside the organization, etc.) and impersonate him/her, urging employees to take action.
Whale phishing
This type of attacks target CEOs or other leadership members. The mechanics are similar: information gathering and impersonation. Cybercriminals use similar email addresses to ask for money transfers or convince employees to download malicious code.
Clone phishing
Another type of email phishing attack, clone phishing takes advantage of business apps that organizations use on a daily basis (e.g. DocuSign). Once cybercriminals detect the apps the organization uses regularly, they send out emails that apparently come from these services.
Email spoofing
This type of attack consists of counterfeiting an email header so that the message appears to have been sent by a legitimate source. These types of emails usually request the victims to pay outstanding invoices, update billing information, verify accounts, or update passwords.
Anti-spam solutions
Email is one of the cheapest and most effective strategies for phishing and spreading malware. Protecting your business against the ever-evolving digital threats has become a priority. Let’s take a look at some noteworthy email security solutions.
Ideal for corporate environments, this software blocks spam before it reaches the inbox. One of the biggest advantages is that it is compatible with all the email providers for both mobile devices and desktops (e.g. Hotmail, Gmail, Outlook, Yahoo, Windows Live Mail, etc.) Among its most notable features, we can highlight:
-
- Offers real-time protection against spam, email viruses, phishing emails, unwanted emails and newsletters
- Operates on Windows 7, 8, 10, Vista, XP
- Unwanted messages can be deleted from the server
- The WHOIS report discloses the real sender and all the hidden links
- Advanced custom filters
- The advanced filters can spot both spam and offensive words
Designed for Macs, this AI-powered spam filtering solution is compatible with a comprehensive list of email systems such as Apple Mail, Airmail, Entourage, Mailsmith, Outlook, Postbox 5, MailMate, or PowerMail. Among its most notable features, we can highlight:
- Uses ML to enhance and customize spam detection over time
- Provides both whitelisting and blacklisting
- Recovers valid messages identified as spam by server junk filters
- Multiple customization options (e.g. colours, layout, mailbox management scripts, etc.)
- Able to decode messages and identify their true nature
Designed for the corporate environment, this spam filter software offers 23 layers of tests to ensure maximum detection rates. Among its most notable features, we can highlight:
- Eliminates false positives
- Provides blacklisting by IP address and range, country, and DNS
- Integrates directly with the IIS SMTP Service and Microsoft® Exchange
- Multi-stage transport filtering
- Provides self-learning whitelisting and whitelist customization
- Offers protection against DHA attacks
- Allows for remote managing and real-time monitoring
Designed for the corporate environment, this anti-spam software not only filters unwanted messages but also protects the system from email-carried malware. Among its most notable features, we can highlight:
- Built upon big intelligence and combined with Skeptic™
- The data loss prevention feature allows managers to control and encrypt sensitive data
- Offers protection against spam, phishing, targeted attacks, and malware
- Uses predictive analysis to detect new threats
- Supports Microsoft Office 365, Google Apps, hosted and on premises Microsoft Exchange, as well as other mailbox services
- Advanced email image control
Tips on how to enhance your organization’s email security
Even though anti-spam software offers enhanced protection against digital threats, there are additional actions you can take to mitigate human error and keep your organization’s files, systems, and data safe.
Use multifactor identification
Using several metrics to authenticate users can increase security and make it more difficult for cybercriminals to bypass authentication. From password manager applications to biometric identifiers, the market offers a wide range of solutions.
Keep privilege control…under control
Errors happen. If your employees have access only to the data they actually need to perform their tasks, a mistake will significantly reduce the extent of the caused damage.
Train your employees
Growing awareness among your employees about digital threats and providing basic training on cyber security topics such as responsible data handling or proper security procedures might save your business a lot of time, money, and stress.
Keep your software functional and updated
No matter how reliable and proficient your cyber security software is, neglecting updates or disabling essential features can provide cybercriminals with the perfect opportunity to act.
Wrap up
Emails have always been a convenient channel for cybercriminals to trick people into disclosing sensitive data or installing malware. Under the COVID-19 pandemic scenario that increased everybody’s connectivity dependence, cybercriminals have perfected their strategies to bypass protection. Even though investing in solid cyber security policies and procedures might help to keep cybercriminals at bay, you should also implement strategies to reduce the risk of human errors. In an ever-evolving and zealous digital threats landscape, the adage Forewarned is forearmed acquires new meanings.